Heat Dissipation of Inverters
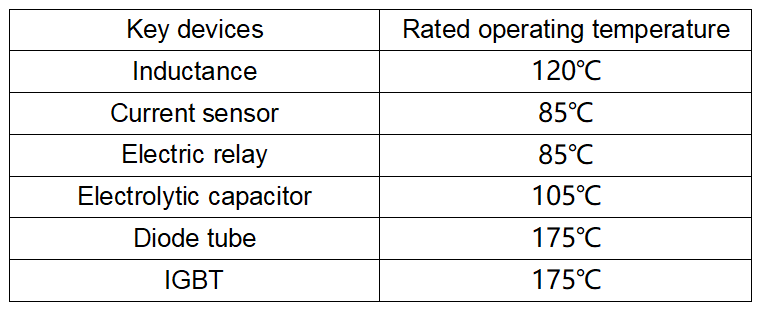
The components in an inverter have their rated operating temperatures. If the inverter has poor heat dissipation performance, as it continues to operate, the heat generated by the components cannot be transferred to the outside, causing their temperature to rise continuously. Excessive temperatures can reduce the performance and lifespan of the components. To keep the operating temperature of the internal components within the rated temperature range and ensure their efficiency and service life, thermal conductive materials are required to transfer the heat from inside the inverter to the outside.
The Overall Structure of the Inverter
Silver has the best thermal conductivity, followed by copper and gold, with aluminum ranking next. Heat sinks are typically made from aluminum mainly because, compared to gold, silver, and copper, aluminum is lightweight, inexpensive, corrosion-resistant, and can be shaped into various complex forms using processing equipment. These properties allow it to meet the many requirements of the electronics and power industries for heat sinks, making it the ideal material for their construction.
By adopting an integrated shell structure, the heat sink is directly and closely connected to the outer shell, allowing the aluminum alloy shell to participate in heat dissipation through two pathways. Since the shell is more involved in the heat dissipation process, the temperature of the inverter casing tends to be relatively high. The advantage of this phenomenon is that the excellent thermal conductivity of the shell enables faster transfer of heat from the inverter's interior through the casing, thereby lowering the internal temperature of the inverter and the components. This helps ensure a longer service life for both the components and the inverter itself.
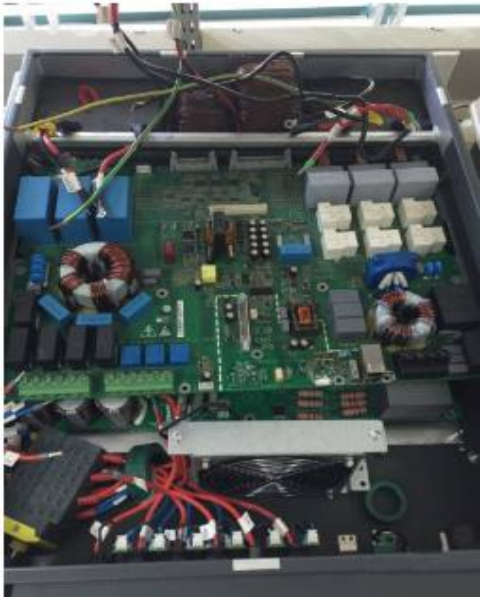
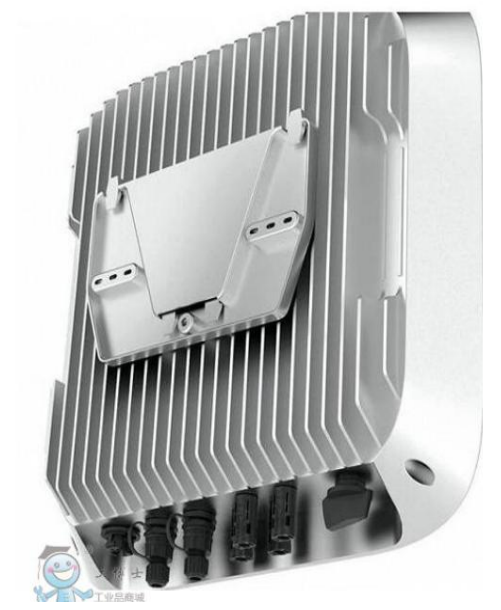


Inverter Cooling Solution
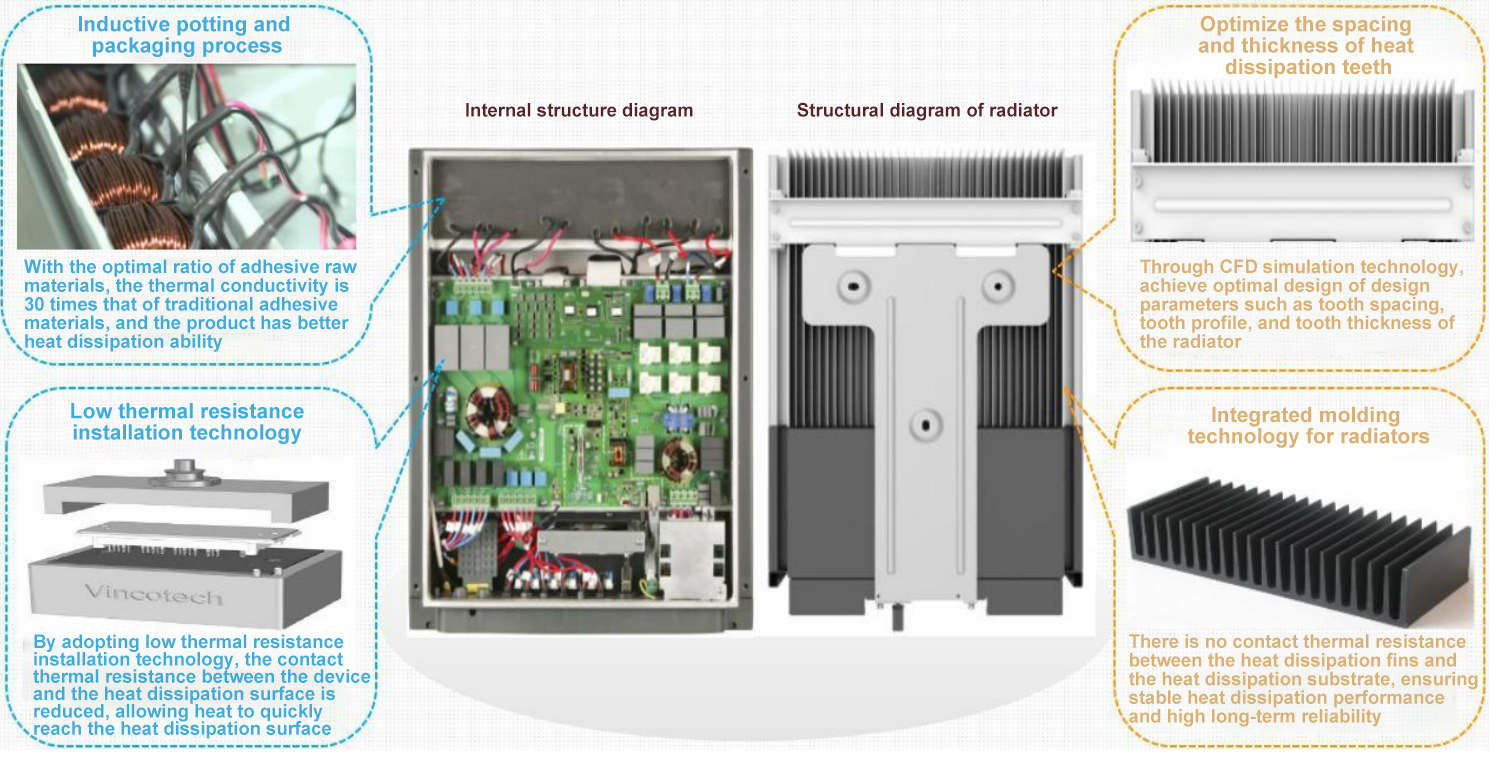
Application of Thermal Conductive Materials in Inverters
Thermal grease
Low thermal resistance and fast heat dissipation.
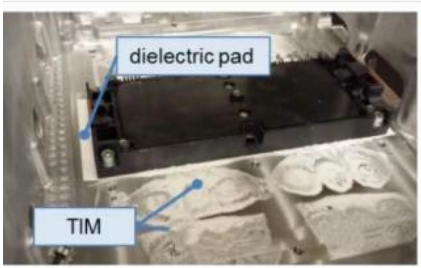
Thermally conductive potting glue
All-round heat dissipation, sealing, shockproof, and corrosion-resistant.

Thermal insulation pad
With base material, cost-effective, resistant to puncture and tearing.
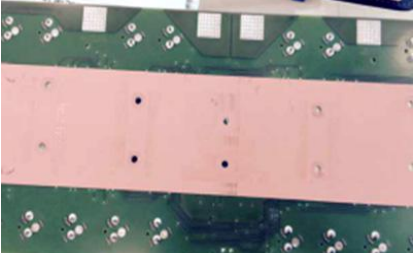
High thermal conductivity silicone pad
Featuring high thermal conductivity, excellent conformity, and low thermal resistance.

-
-
Next one:Energy Storage Battery System

















