Thermal conductive materials play a crucial role in the electronics industry, with thermal conductive silicone grease and thermal conductive gel being two common types. Both of these thermal interface materials are in a paste-like form, but how do you choose between thermal conductive silicone grease and thermal conductive gel? Let's delve into the differences between these two materials.


Thermal grease
Thermal conductive silicone grease, also known as thermal paste or thermal compound, is composed of 'silicone oil + filler.' The filler consists of finely ground powders such as zinc oxide, aluminum oxide, boron nitride, silicon carbide, aluminum powder, and others. The silicone oil ensures a certain level of fluidity, while the filler fills in the tiny gaps between the CPU and heatsink, ensuring thermal conductivity. It has a wide range of applications and is suitable for almost any heat dissipation requirement.

Application
Applied for thermal conduction between ICs, CPUs, MOSFETs, IGBTs, and heatsinks, such as PCs, LEDs, DVDs, power supplies, communication products, network terminals, consumer electronics, power devices, storage devices, LED lighting fixtures, etc.
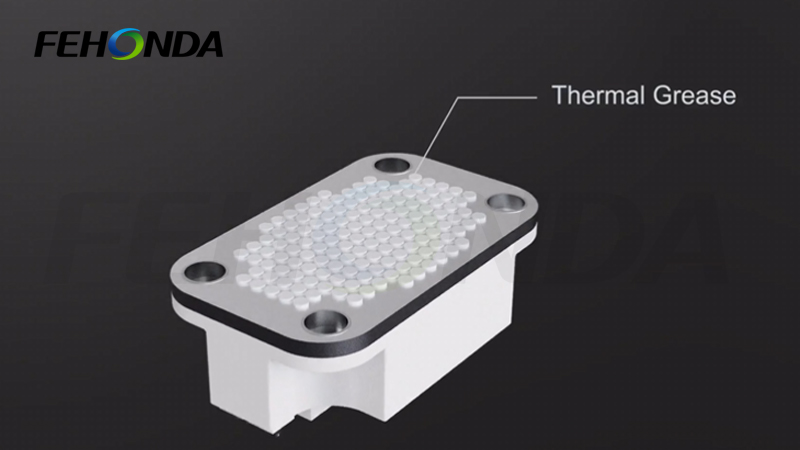

< IGBT module Feihongda thermal grease application diagram >
Thermal gel
Thermal conductive gel is a gel-like silicone-based thermal conductive material, available in single-component and two-component combinations. It is made by stirring and mixing silicone resin, cross-linking agent and thermal conductive filler. It is suitable for microscopically uneven contact surfaces. The colloid is formed according to the shape of the structure, with strong surface conformability and sufficient gap filling. The product has excellent insulation voltage resistance and high and low temperature resistance, high reliability in long-term use, and can be automatically dispensed to achieve automated operations.

Application
It is used in the contact surface between heating elements (power tubes, thyristors, electric heating piles, etc.) and heat dissipation facilities (heat sinks, housings) in various electronic products and electrical equipment, playing an intermediate role in transferring heat and moisture, and having dust-proof, corrosion-resistant, and shock-resistant properties.
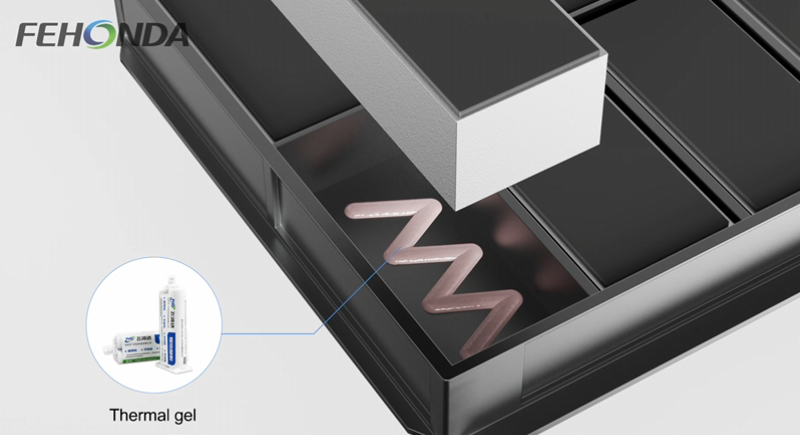

<New energy vehicle battery pack>
Difference between thermal grease and thermal gel
Thermally conductive gel is easier to operate than thermally conductive silicone grease. The general use of silicone grease is screen or steel plate printing, or direct brushing, and because of its certain fluidity, it is generally not used in occasions with a thickness of more than 0.2mm. Thermally conductive gel has a certain degree of adhesion, can be compressed into various shapes, and will not have the problem of oiling and drying, and has certain advantages in reliability.
Thermally conductive gel has certain advantages in continuous operation. The commonly used continuous use method is a dispensing machine, which can achieve fixed-point quantitative control, saving labor and improving production efficiency.
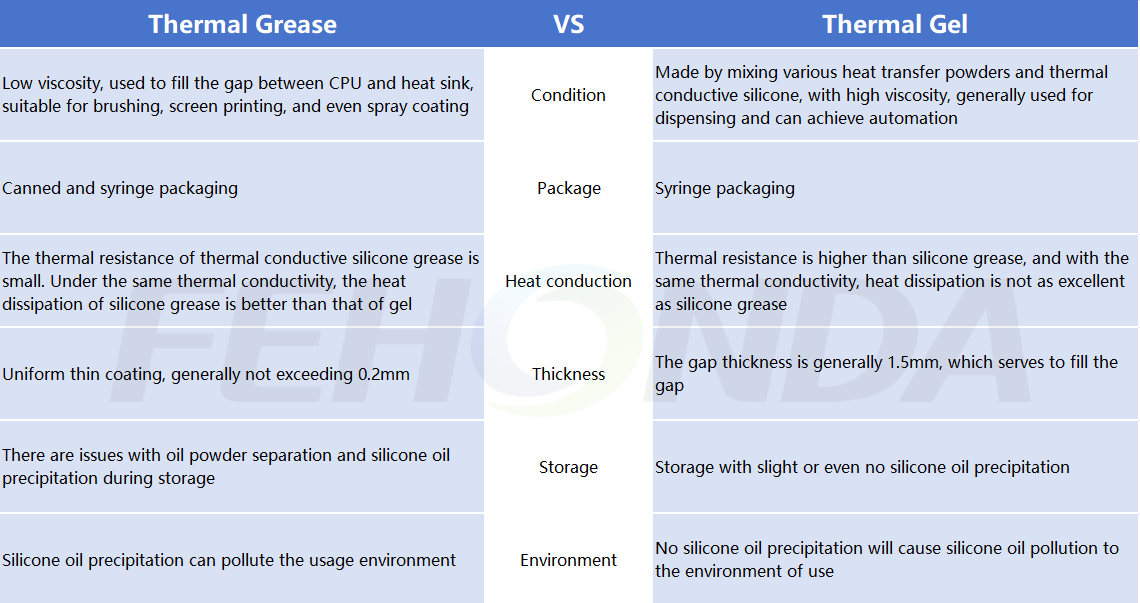
There are many differences between thermal grease and thermal gel, such as application scenarios, lifespan, insulation performance, etc. Therefore, thermal gel is not thermal grease, and both have their own uses. Users can choose the appropriate thermal conductive material according to their own product characteristics and product structure requirements.





